The Cannabinoid That Changed the Way We Understand Cannabis

Ask someone what causes cannabis to produce its familiar effects, and most will immediately say “THC.” But what is THC, really? Why does it affect the mind? And why has it been the focus of research, policy, and cultural conversations for decades?
Understanding the journey from farm to feeling starts with one critical distinction. If you’ve ever wondered about the difference between the cannabis you buy and the cannabis you consume, our article THCA vs. THC: A Complete Guide breaks down the science, benefits, and conversion process clearly.
Let’s explore THC in a deeper, more holistic way, beyond simple definitions.
🌱 What THC Actually Is
THC (delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol) is the primary intoxicating cannabinoid in cannabis. It’s one of the best-studied compounds in the plant and plays a major role in how cannabis affects perception, mood, coordination, and cognition.
But THC is more than just a psychoactive molecule.
It acts as a chemical messenger that interacts with one of the most important systems in the body: the endocannabinoid system.
🧠 How THC Interacts With the Brain
Inside the human body, the endocannabinoid system (ECS) helps regulate:
- Mood
- Memory
- Pain perception
- Appetite
- Sleep
- Stress responses
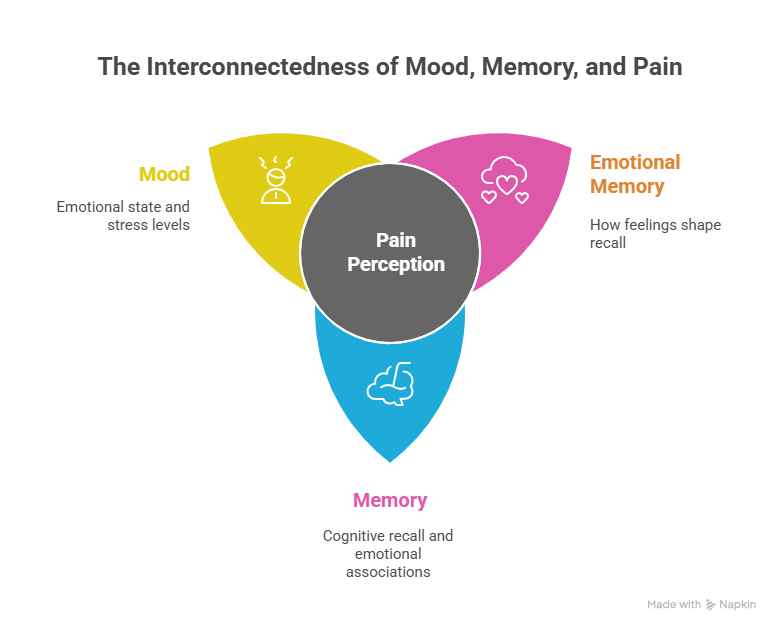
The ECS uses naturally occurring compounds called endocannabinoids, which bind to receptors throughout the brain and body.
THC mimics some of those compounds, especially anandamide (often nicknamed “the bliss molecule”). When THC binds to CB1 receptors, it changes the way neurons communicate. That’s why people experience:
- Altered perception
- Changes in time awareness
- Enhanced sensory input
- Increased appetite
- Impaired short-term memory
The experience varies widely among individuals.
🔥 Why THC’s Effects Can Differ So Much Between People
Several factors influence how THC affects someone:
- Method of consumption (inhaled vs. ingested)
- Individual metabolism
- Tolerance levels
- Cannabinoid and terpene ratios in the plant
- Set and setting (environment and mindset)
For example, edibles produce a slower onset but often more intense effects because the liver converts THC into 11-hydroxy-THC, a metabolite with stronger psychoactive properties.
⚖️ THC and U.S. Regulation
THC is regulated at both state and federal levels in the U.S.
Federally, THC above certain thresholds is categorized as a controlled substance.
States vary widely:
- Some allow full adult-use cannabis
- Some allow medical use only
- Some have mixed or limited frameworks
- Others prohibit possession altogether
Because cannabis laws evolve rapidly, individuals and businesses must stay updated on local regulations.
🧪 THC in Lab Testing
Cannabis testing labs measure:
- Delta-9 THC
- THCA (the precursor)
- Total THC (potential THC after heating)
This helps consumers, regulators, and researchers understand potency and safety.
⚠️ Public-Health Considerations
THC can impact:
- Motor coordination
- Reaction time
- Short-term memory
- Heart rate
- Anxiety levels in some individuals
Healthcare professionals advise exercising caution, especially for people with underlying health conditions, pregnant individuals, or those taking medications.
📝 Bottom Line
THC is central to the cannabis experience, scientifically and culturally. It continues to be studied for its effects on the brain, its therapeutic potential, and its role in shaping cannabis regulations across the U.S.
